Vierailin syyskuussa Satu Kivelän Havaintoja muutoksesta ja merkitysten etsijät -ohjelmassa YLE Radio1:ssä keskustelemassa naisyrittäjyydestä. Ohjelma rakentui teorian ja käytännön vuoropuhelulle:…
Tekijät | Authors

The Growing Significance of Soft Skills in the Green Transition: More Than Just Technical Know-How?
Traditionally, hard skills have been considered essential, yet, several studies highlight the crucial role of soft skills in rapidly changing working environments.
The SOFTEN project emphasises the perspective that higher education institutions must be able to develop students’ skills to act in the green transition. The Project aims to equip students, educators, and professionals with the interpersonal competencies needed to tackle the environmental and social challenges of the future, fostering an education system that aligns with evolving global demands.
Nowadays, the unfolding climate emergency and mega trends such as the globalisation, digitalisation and transition to a low-carbon economy are reshaping and transforming the way that young graduates and employees collaborate with each other and respond to challenges of their current rapidly changing workplace. Climate change is progressively changing the nature of work in various occupations and the skills required of many workers, especially in the STEM fields.
The development of new and different competences for green jobs is considered a critical parameter
The development of new and different competences for green jobs is considered a critical parameter for ensuring that the transition to a green economy is inclusive and fair, by matching supply and demand for skills (Global Deal, 2023). Therefore, the ability to develop these skills as part of a holistic approach to the ’greening’ of the economy is essential for educators, as their students are future workers and potential change agents in the green industry. At the same time, more knowledge about the context in which soft skills are used is of great interest.
Highlights from the SOFTEN Framework
The first concrete result of the SOFTEN project is a conceptual and research-based framework that includes both theoretical knowledge and findings from research activities. The primary goal behind these activities is to draw the attention of STEM academic community and of green industry stakeholders about the critical role of soft skills as part of green competences and green transformation process.
Another primary objective of SOFTEN research study is to understand better the most important trends and opportunities in STEM Higher Education Area (HEA) and dive into the needs of green companies in six European countries in relation to the following topics:
- Current level of awareness from the side of STEM educators, students and green representatives on the concept of soft skills as well as their role and relation with green competences and green transition.
- Needs and gaps on soft skills’ development within STEM academic programmes and across a diversity of green economy sectors.
- Identification of driving factors for soft green skills promotion and development in STEM curricula.
- Initiatives and good practices on soft skills development in universities and green economy entities.
Following the main analysis of research findings, the report provides a summary of conclusions and lessons learnt from the whole study, a detailed bibliography with all used online sources from each chapter and five Annexes, including the reporting templates that were designed for each research activity and the developed interview guide.
Considering all mapped trends and collected opinions that are presented in the report, it seems that soft skills are becoming critically important for many fields and especially for the advancement of STEM students’ green career and professional development. Notwithstanding the application of relatively limited and scattered initiatives on soft skills’ development recorded at university level and as part of some green companies’ operation, the connection of these ‘transferable’ skills with green transition is not explored that much in the participating countries.
It seems that soft skills are becoming critically important for many fields and especially for the advancement of STEM students’ green career and professional development.
At the same time, existing challenges (e.g., traditional structure in several STEM curricula, lack of educators’ competences and capacity to perform trainings on such skills and the medium-level awareness of surveyed STEM students for the connection of soft skills and their role to green profession) underline the necessity for additional steps and strategies that need to be adopted by the technical academic programmes.
As shown in Figure 1, almost 50 % of students (48 out of 98 respondents) seem not to be aware of the offering of opportunities for such skills-related trainings in their respective educational programme.
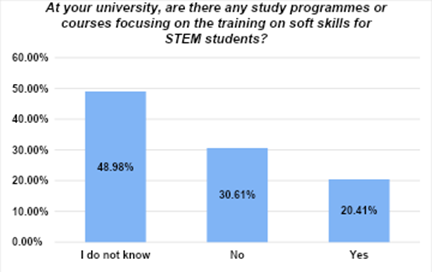
FIGURE 1. LEVEL OF STEM STUDENTS’ AWARENESS FOR SOFT SKILLS TRAININGS IN THEIR STUDIES
In addition, organised solutions and effective pathways to tackle soft skill shortages and gaps vary from one country to another, depending on stakeholders’ needs and interest at national level. Apart from each country’s particularities, the study’s results call for a revision of existing STEM academic curricula and an improvement of qualification standards and training opportunities.
The study’s results call for a revision of existing STEM academic curricula and an improvement of qualification standards and training opportunities.
As skills shortages persist and the low level of STEM educators’ capacity building in interdisciplinary methods pose further barriers to enhance students’ green soft skills competences, coherent and forward-looking policies within STEM educational curricula, through a combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches and public-private partnerships for skills and capacity development, are more than essential to meet successfully the green labour market’s needs. The students’ survey also highlights their level of interest in developing further soft skills in the context of green thinking though university curricula and the extent of their agreement or disagreement in a list of channels/methods based on which they prefer to learn more and cultivate soft ‘green’ skills.
Figure 2 showcases that there were positive responses in terms of their interest to further enhance their soft ‘green’ skills in the context of their curricula reached, as aggregate, around 75 % of total number of STEM students (4: agree with almost 37 % and 5: strongly agree with almost 35%).
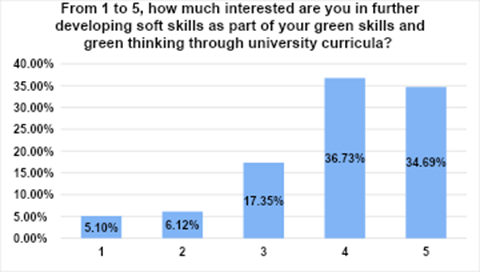
Figure 2. LEVEL OF STUDENTS INTEREST ON SOFT SKILLS
Solutions and Major Accomplishments of the SOFTEN Project
A key achievement of the SOFTEN project is a free of charge learning environment designed for educators, educational managers and professionals, offering interactive modules and practical tools to help integrate interpersonal and environmental skills into STEM curricula.
The Project offers interactive modules and practical tools to help integrate interpersonal and environmental skills into STEM curricula.
Resources can be accessed freely on the https://greensoftskills.eu/ website and online module from the Politecnico di Milano Open Knowledge website https://www.pok.polimi.it/ (free registration required). These provide pedagogical methodologies and resources such as De Bono 6 thinking hats and Problem Based Learning, aligning teaching practices with the goals of the green economy.
The project aims to create collaborative networks between higher education institutions and industries, fostering innovation and commitment to sustainable practices.
The project not only empowers educators but also aims to create collaborative networks between higher education institutions and industries, fostering innovation and commitment to sustainable practices. This systemic approach reflects the urgent need to train leaders and specialists capable of steering the transition to a more sustainable and inclusive economy.
We invite educators, students and educational managers to explore the resources available through the SOFTEN project and to join this transformative initiative. For more information and updates, follow the project on social media, including Facebook and LinkedIn, or visit the official project website.
The project is funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the National Agency (NA). Neither the European Union nor the NA can be held responsible for them. Project No. 2022-1-PL01-KA220-HED-000085725.
SOFTEN Project: Integrating Soft Skills into STEM for a Sustainable Future
The SOFTEN Project is an Erasmus+ initiative co-funded by the European Union, designed to integrate soft skills into STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) academic programs. Focused on enabling the transition to a sustainable green economy, the project aims to equip students, educators, and professionals with the interpersonal competencies needed to tackle the environmental and social challenges of the future, fostering an education system that aligns with evolving global demands.
Led by the Wroclaw University of Environmental and Life Sciences (Poland), the international consortium of SOFTEN includes prestigious institutions and organisations such as Politecnico di Milano (Italy), Xwhy / Agency of Understanding (Lithuania), Kaunas University of Technology (Lithuania), Turku University of Applied Sciences (Finland), Stimmuli for Social Change (Greece), and INOVA+ (Portugal).
Since November 2022, these organisations have collaborated to create educational resources aimed at fostering essential competencies, including, among others, communication, leadership and teamwork. The project is set to conclude in October 2025.
Artikkeli on osa Yrittäjyys ja arvonluonti -tutkimusryhmän julkaisuja.








